Obstructive Sleep Apnoea: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Sleep Apnoea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people around the world. This guide will explore Obstructive Sleep Apnoea, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, health risks, and treatment options.
What is Sleep Apnoea?
Sleep Apnoea is a serious medical condition that involves repetitive breathing pauses during sleep. The pauses can last from a few seconds to minutes throughout the night and these pauses significantly reduce the oxygen levels of the individual. These breathing interruptions also disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to fragmented sleep, and can cause various other health complications.
Types of Sleep Apnoea
Central Sleep Apnoea (CSA) occurs when the brain fails to send appropriate signals to the muscles responsible for breathing. Unlike OSA, which is caused by a blocked airway, CSA is caused by problems in how your brain controls breathing. This disruption leads to intermittent pauses in breathing during sleep.
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA) is the most common type and occurs when the airway is partially or completely blocked during sleep.
OSA is classified by severity based on the number of apnoeas and hypopnoeas (breathing interruptions) that occur per hour of sleep for ten seconds or longer.
Apnoeas: When the throat muscles and soft tissues relax and cause a full airway blockage.
Hypopnoeas: A partial blockage of the airway that reduces the airflow by 50%.
OSA severities:
- Mild is defined as 5-15 apnoeas and/or hypopnoeas per hour.
- Moderate is defined as 5-30 apnoeas and/or hypopnoeas per hour.
- Severe is defined as 5-30 apnoeas and/or hypopnoeas per hour.
It is considered normal for everyone to have between 0 and 4.9 every hour.
Signs & Symptoms of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
- Gasping or choking during sleep: When the airway is blocked, your brain will eventually wake you to catch your breath; this can cause you to gasp and choke.
- Breathing pauses: Episodes of Sleep Apnoea, are observed as breathing pauses and are reported by someone else.
- Snoring: Snoring occurs when the airflow is blocked, causing the surrounding tissues vibrate, producing the snoring sound. However, not everyone who snores loudly has OSA. Some people may snore due to other factors, such as nasal congestion, alcohol consumption, or certain sleeping positions.
- Daytime fatigue: The pauses in breathing and reductions in airflow cause the brain to react to the oxygen drop by waking you up. This repeated cycle creates fragmented sleep, leading to fatigue.
- Anxiety & Depression: The reduced sleep caused by Sleep Apnoea is associated with mental health conditions. However, the extent to which sleep deprivation may be related to these conditions is not clear.
- High Blood Pressure: OSA causes sudden drops in blood oxygen levels, increasing blood pressure and straining the heart. The continuous strain increases the risk of high blood pressure (hypertension).
- Low libido: Reduced sleep can create daytime fatigue, and when combined with general depression, it can affect the libido.
- Irritability: Sleep loss can lead to changes in mood and cognition. People with Sleep Apnoea have lower levels of GABA and abnormally high levels of glutamate. While GABA is a mood inhibitor and helps people keep calm, glutamate has the opposite effect. Elevated glutamate levels increase stress and stop the brain from functioning correctly.
- Difficulty concentrating: Sleep Apnoea can reduce cerebral metabolism within the prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for cognition (concentration).
- Poor Memory: It is suspected that people with a lack of restorative sleep have difficulty converting short-term memory to long-term memory.
- Frequent urination: Nocturia (frequent toilet visits during the night) is also prevalent in Sleep Apnoea patients. This can be due to a combination of things, including increased fluid retention, increased cardiac stress, hormones and poor sleep.
- Morning headaches: Consistent oxygen deprivation can cause morning headaches. Hypoxic headaches are the most common headaches associated with OSA and often do not last long.
- Impotence: Scientists don’t know exactly why men can have erectile dysfunction, but lack of sleep can cause testosterone to drop. This testosterone dip, plus the lack of oxygen, could be the cause. Both are important for a healthy erection. Stress, anxiety, and fatigue can also be contributing factors.
If you have OSA, you may have no memory of your interrupted breathing during the night.
Sleep Apnoea Causes
Weight: Excess body fat increases the fat around the throat and neck, which can strain the throat muscles. This increased fat can make breathing more difficult during sleep, causing OSA.
Age: As we age, the springiness of our muscles reduces, making developing the condition more likely.
Medication: Many medications can have a sedative effect and relax the throat muscles. This induces sleep and increases the likelihood of the airway collapsing.
Alcohol: Drinking alcohol before going to sleep can relax the throat muscles, increasing the risk of an airway obstruction.
Smoking: Nicotine worsens sleep and inflames the upper airway.
Hormonal changes: Hormones hugely impact the quality of our sleep and how we breathe. For example, hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy and menopause can relax the throat muscles.
Nasal congestion: OSA is more prominent in those with a deviated septum, hayfever and allergies. This is because it makes breathing more difficult.
Genes: A family history of OSA can make you more likely to develop the condition.
Diagnosing Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
Diagnosing Sleep Apnoea typically involves a combination of evaluating medical history and conducting a sleep studies.
An overnight Sleep Apnoea test can be done privately or through an NHS sleep clinic. You can request an NHS sleep test from your GP. To begin this process, you must make multiple appointments with your doctor, collect and return the equipment, and have one night of sleep assessed.
However, it can take months to get an appointment and weeks before you receive results. The results may be shared with the DVLA and your doctor if it is confirmed that you have OSA. In 2020 it was reported that OSA sufferers in the UK are waiting for up to two years to receive the treatment they require through the NHS (1).
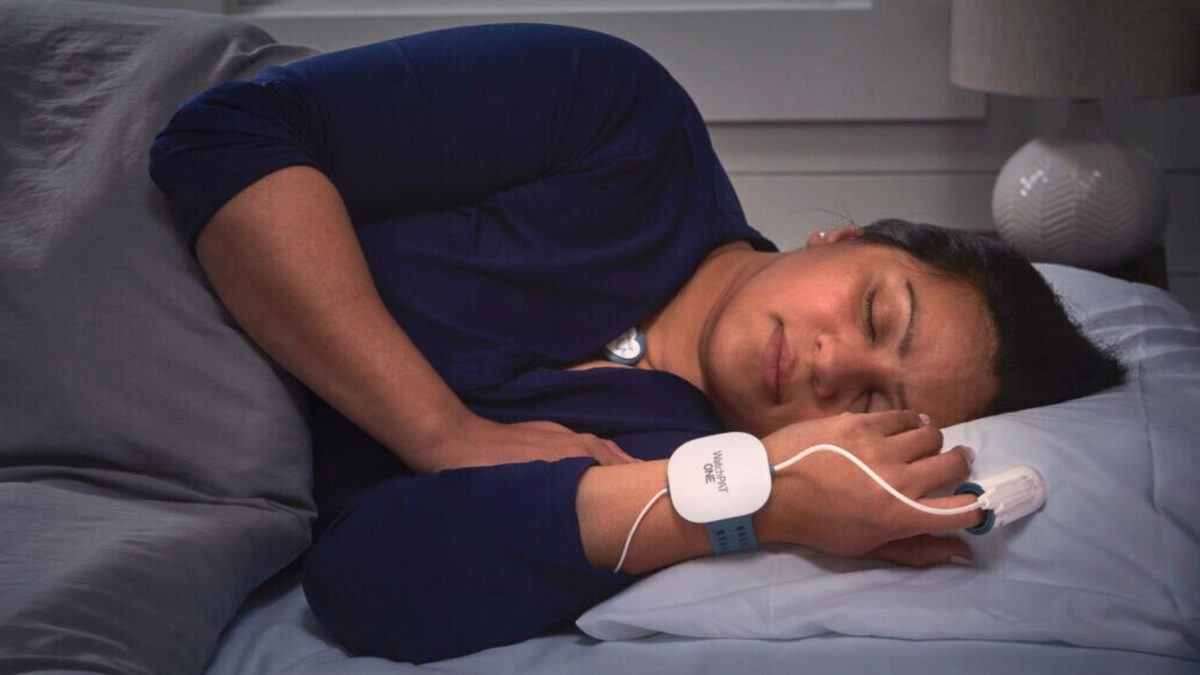

Private In-Home Sleep Test
Our private Sleep Apnoea Test uses medical-grade equipment to assess your sleep. The small and simple device is worn overnight from the comfort of your own home. Our specially trained NHS sleep specialists evaluate the results, which are returned within two working days of completing the test. Results are sent directly to you and will not be shared with your doctor or the DVLA.
Many of our customers begin their treatment as soon as the day after receiving their sleep test results.
How to treat Sleep Apnoea
Effective management of Sleep Apnoea is crucial for improving quality of life and reducing associated health risks such as heart disease and excessive daytime sleepiness. The best treatments for Obstructive Sleep Apnoea are detailed below:

CPAP Therapy
CPAP therapy (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) is the most effective treatment for OSA. It requires a CPAP machine, mask and tube, which supplies pressurised air to prevent the airway from collapsing.
CPAP is the gold-standard treatment method, with a variety of different machines and masks available. We supply a CPAP equipment from leading brands to suit the requirements of as many users as possible.
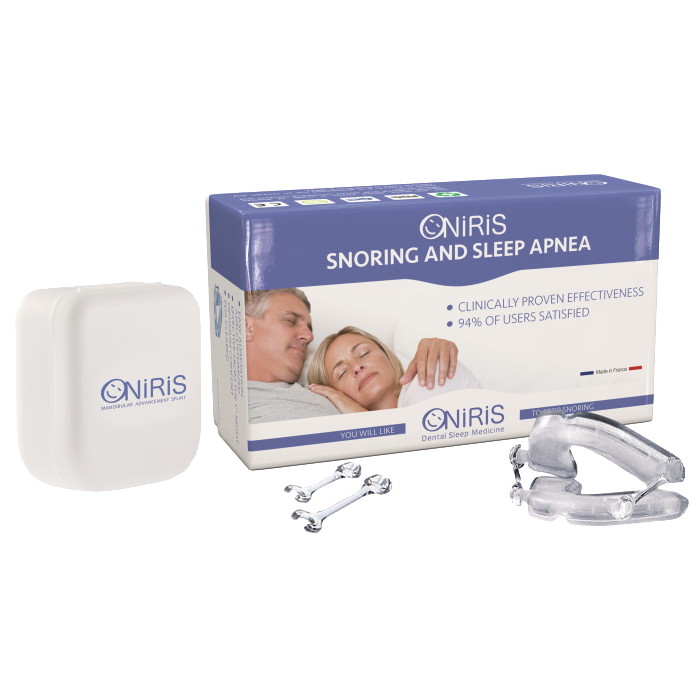
Mandibular Advancement
Oral appliances, known as Mandibular Advancement Devices (MADs), are custom-fitted devices worn during sleep. They reposition the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open.
MADs use the boil and bite method for a personalised and comfortable fit.
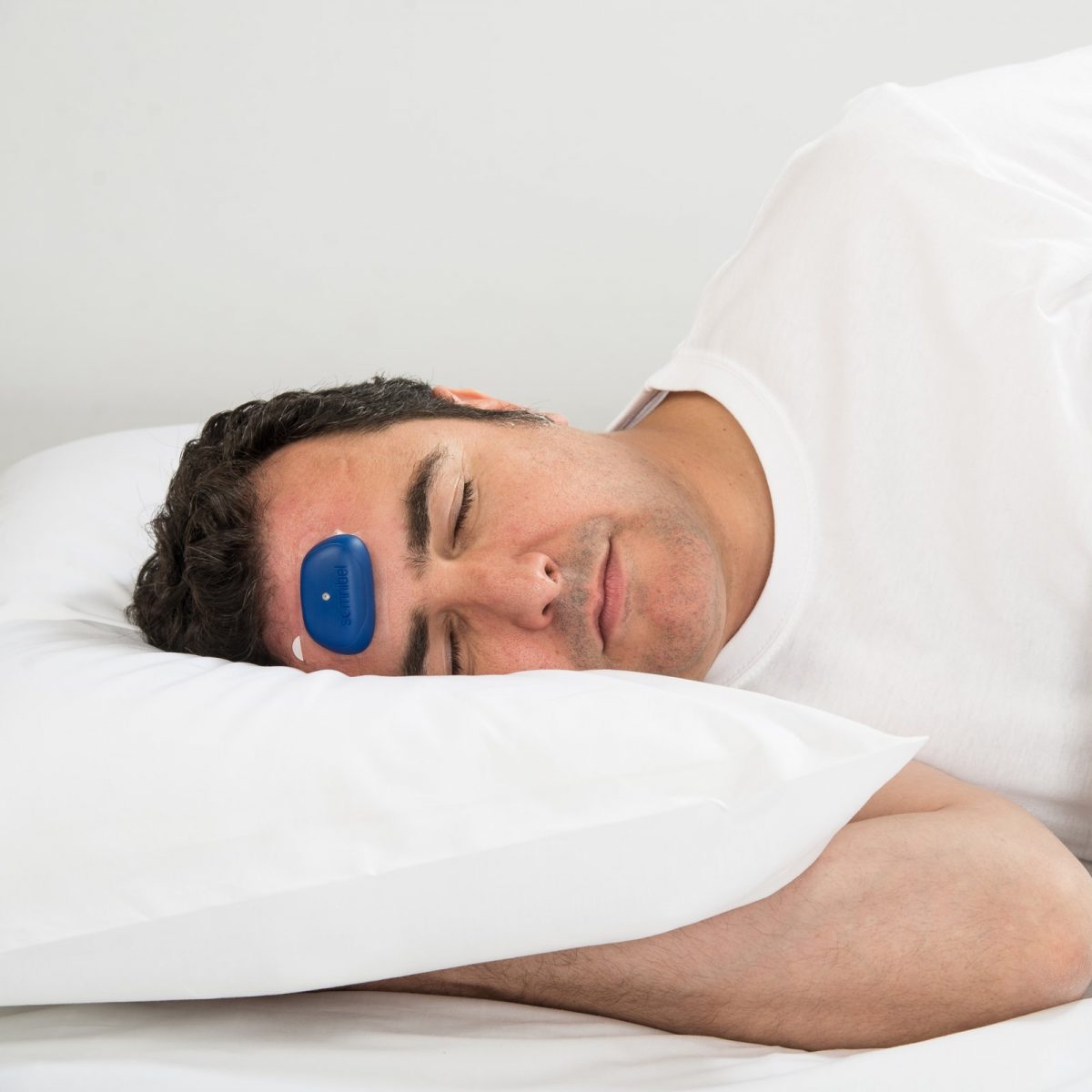

Positional Therapy
Positional therapy is designed for those who experience Sleep Apnoea episodes more prominently when sleeping on their back. The lightweight therapy encourages the user to roll back onto their side if they roll onto their back.
The Somnibel Positional Sleep Therapy Trainer is a small forehead device that detects when you roll onto your back. When you do so it produces a light vibration to encourage you to turn back onto your side.
Surgery and Other Interventions
Surgery may be considered for severe cases or when other treatment options are ineffective. Procedures may involve removing the excess tissue from the throat, correcting structural differences, or moving the jaw.
Natural Remedies for Sleep Apnoea
There are many natural ways to reduce the symptoms of Sleep Apnoea. However, the effectiveness is dependent on the severity.
Reducing weight/neck circumference
Research has found that men with a neck circumference above 17 inches and women with a neck circumference above 15 inches are much more likely to develop Sleep Apnoea (2).
Many people with severe cases of OSA are overweight or obese, as excess weight puts pressure on the upper airway.
Quitting smoking
Smoking can contribute to the development of OSA and make the condition worse. Smoking can cause inflammation and swelling in the upper airway, narrowing the airway and making breathing more difficult. It can also weaken the muscles in the upper airway, leading to further narrowing of the airway. Smoking can also increase the production of mucus in the airway, which can further obstruct breathing.
Alcohol
Alcohol is a sedative which can relax the muscles in the throat and cause the airway to become blocked during sleep. Regularly consuming a high amount of alcohol before you sleep disrupts your REM sleep, increasing the risk of OSA by 25% (3).
Changing diet
Obesity is a key risk factor for OSA. Eating an unhealthy diet that contributes to excess body weight may cause or worsen your symptoms. Eating a more nutritious diet can improve your weight, well-being and overall health.
Medications and sedatives
Certain medications can aggravate sleep disorders. It is worth checking with your doctor if your medication could be affecting your sleep.
Changing sleeping position
Sleeping on your side is generally advised for those with sleep problems as it comfortably opens the airway.
Sleep hygiene
Good sleep hygiene is essential for individuals with or without a sleep problem. Good habits include a consistent sleep schedule, a sleep-friendly environment, limiting screen time, and practising relaxation techniques.
Regular exercise
A healthy diet and regular exercise are important aspects of managing symptoms and improving overall sleep quality.
Long-term health risks of OSA?
When left untreated, it can impact different parts of the body and increase the risk of other health conditions.
Heart conditions:
The repeated drops in oxygen levels and increased carbon dioxide levels during apnoea episodes can lead to heart disease, arrhythmias, heart attacks, heat failure and stroke. The reduced oxygen intake also makes the heart work harder, increasing your heart rate.
Cognitive effects:
OSA can negatively impact cognitive function and overall brain health. Intermittent breathing interruptions disrupt the normal sleep architecture, impairing memory, attention, and concentration. Additionally, untreated Sleep Apnoea is associated with an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Impact on teeth
As you are more likely to grind your teeth and breathe through your mouth, it can result in cracked teeth and cavities. You are more likely to have high blood pressure, depression and a lower sex drive.
Decreased life expectancy
People with OSA are more likely to die prematurely. The physical effects lead to systemic inflammation (affecting the whole body), which is known to cause several chronic diseases.
Metabolic Consequences:
Sleep Apnoea is closely linked to metabolic disorders, including insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and obesity. Disrupted sleep patterns and hormonal imbalances can contribute to weight gain and difficulty maintaining a healthy metabolic profile.
Impact on Mental Health:
Sleep Apnoea has been associated with mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and mood disorders. Sleep disturbances and oxygen deprivation can disrupt the regulation of chemical messengers and hormones, contributing to the development or worsening of these conditions.
Relationship with other conditions:
It is commonly seen in individuals with type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity, and certain breathing conditions such as asthma and COPD.
Treating OSA may have a positive impact on managing these connected conditions.
Decreased road safety
Lack of sleep increases the risk of falling asleep while driving. In fact, statistics show that falling asleep at the wheel and tiredness cause as many as 300 deaths each year (4).
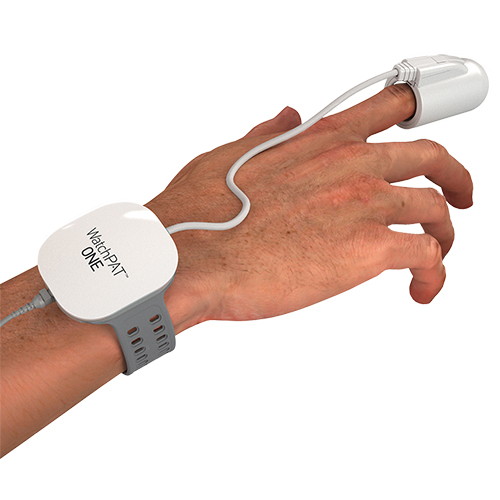
In-Home Sleep Test
Sleep Apnoea is a common sleep disorder with significant health implications. Recognising the signs and symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment is vital for effectively managing the condition. Remember, proper sleep is the foundation of good health.
If you suspect that you have Obstructive Sleep Apnoea, then an in-home Sleep Test can provide a quick, convenient and affordable way to have it confirmed. Within a week you would be able to begin treatment and enjoying deep, restorative sleep again. All studies are independently analysed by experienced NHS-qualified sleep professionals, and use the WatchPAT recording device for unrivalled accuracy.

