Fact Checked
Intus Healthcare’s writers, customer service team, and sleep experts review and ensure this information is accurate.
Last updated on March 27th, 2024 at 08:59 am
Does a CPAP machine stop snoring?
Yes, using a CPAP machine can reduce or eliminate snoring. Allowing you and your bed partner to get the sleep you deserve.
A CPAP machine should also drastically reduce noise levels compared to loud snoring. Modern CPAP machines are quiet at only 30 dB compared to the average snoring volume of 50-60 dB.
How does a CPAP machine stop snoring?
CPAP machines work by providing a continuous stream of pressurised air through a mask that is worn either over the nose or over the nose and mouth. The pressurised air helps to keep the airways open and prevents snoring by reducing the vibration of the soft tissues in the throat.
Want to try CPAP to stop snoring?
Take our fast and accurate In-Home Sleep Test to determine how effective CPAP therapy will be for you. Your results will be with you within 2 working days.
Ready to choose your CPAP machine? At Intus Healthcare, we provide equipment from leading brands. Available with next-day nationwide delivery.
What causes snoring?
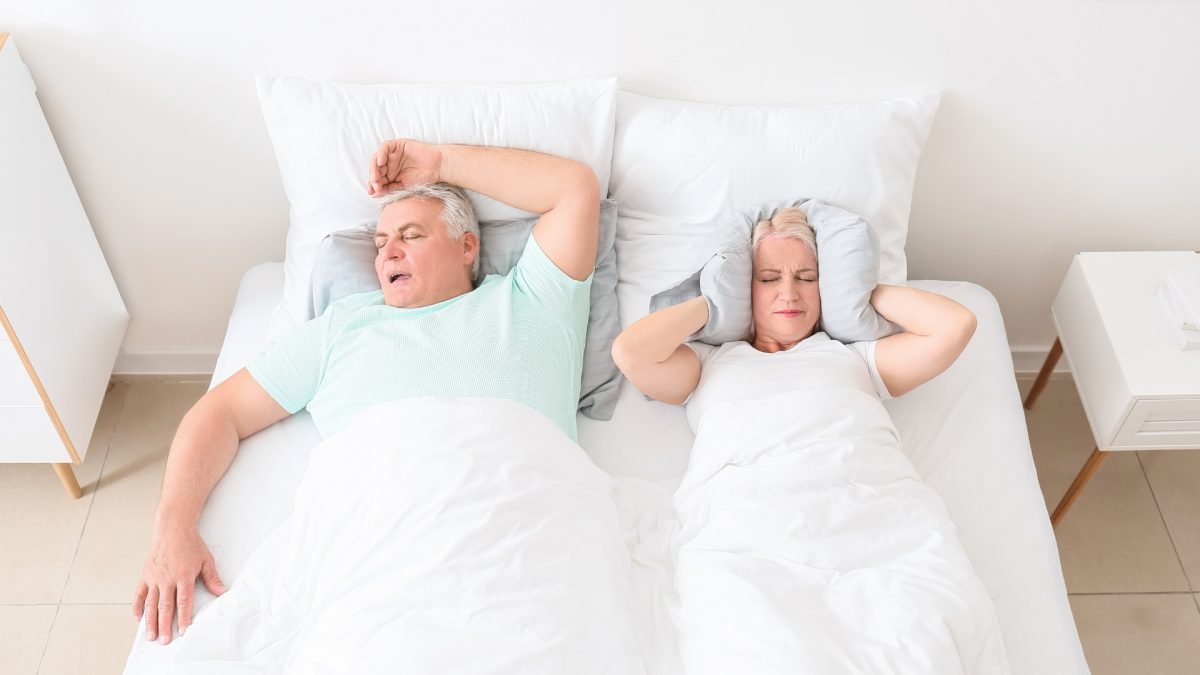
Snoring is a sound produced by the vibration of tissues in the upper airway during sleep. It is usually caused by a narrowing of the airway due to the relaxation of the muscles at the back of the throat. Snoring can be caused by a range of factors. These include obesity, alcohol consumption, smoking, allergies, sinus problems, anatomical issues, and sleep deprivation.
Why is snoring bad?
Snoring can be bad for your health because it can disturb your sleep, leading to fatigue, irritability and daytime sleepiness. It can also be a sign of a more serious health issue, such as Sleep Apnoea, which can increase the risk of high blood pressure, stroke, heart attack and other cardiovascular problems.
Additionally, snoring can cause significant disruption to the sleep of a bed partner, leading to sleep deprivation and a drop in overall quality of life.
Is snoring always a symptom of Sleep Apnoea?
No, snoring is not always a symptom of Sleep Apnoea. Snoring can be caused by a number of different factors, such as being overweight or having a blocked or narrowed airway. Sleep Apnoea is a disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, and it is characterized by loud snoring, frequent pauses in breathing, and excessive daytime sleepiness.
The cause of snoring should be addressed to determine if Sleep Apnoea is the primary cause. Sleep Apnoea is a condition which is treatable and, when treated, can eliminate a range of issues, not least snoring.
Getting tested for Sleep Apnoea
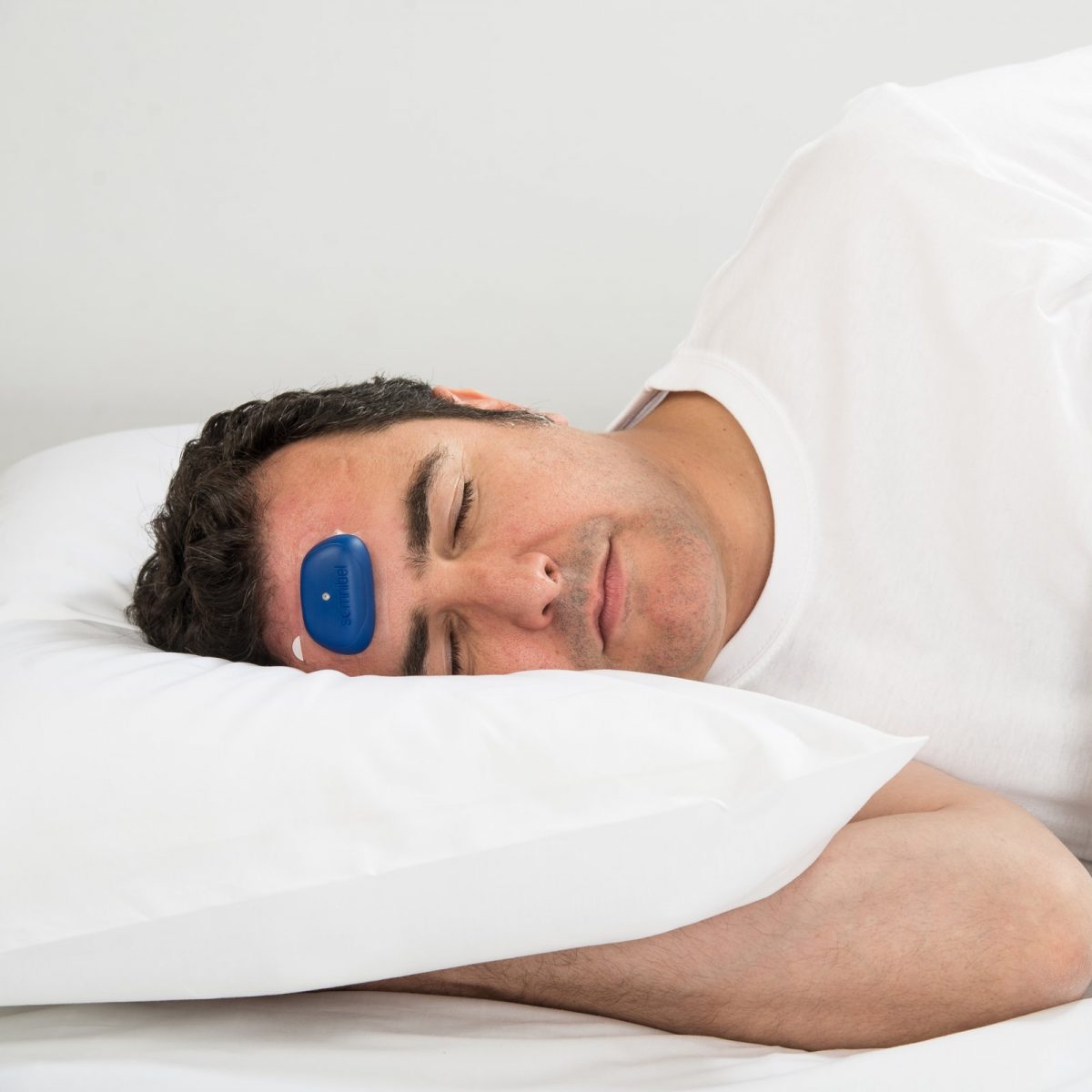
One of the first steps in understanding the cause of your snoring is to take a sleep study or a sleep test. By taking part in an overnight sleep test at home, it is possible for a sleep technician to determine if you are suffering from Sleep Apnoea and if this is the cause of snoring. The test will confirm or rule out the presence of Sleep Apnoea, making it possible for you to start treatment or seek other resolutions to your snoring immediately.

In Home Sleep Test
The Intus Healthcare In Home Sleep Test monitors your blood oxygen levels, heart rate, body position, body movements, snoring intensity, and crucially your Peripheral Arterial Tone – a key physiological signal that can indicate respiratory disturbances during sleep.
All treatment options for Sleep Apnoea require a sleep test to have been taken. This service provides a quick, convenient way of having your sleep assessed by a qualified sleep professional.
Occasional snoring
Even semi-regular or occasional snoring can have an impact on your sleep and the sleep of a bed partner. If you would like to look at ways to reduce snoring, there are some lifestyle changes you can try. These include:
Sleeping position – The position you sleep in can influence the benefits of your therapy. Sleeping on your back can encourage snoring, whereas sleeping on your side can help to keep your airway open. The result? Reduced or eliminated snoring. If you struggle to sleep on your side, consider using a positional sleep trainer.
Weight loss – Obesity and being overweight are common traits in people who snore. Losing weight can alleviate snoring by reducing the fat around the diaphragm. Excess weight around the throat and neck can increase snoring by causing the airway to narrow. Obesity and being overweight also increase the risk of developing Sleep Apnoea and cause more apnoeas and hypopnoeas (breathing pauses). Around 20% of people who are obese suffer from Obstructive Sleep Apnoea.
Reduce alcohol consumption – Drinking alcohol late in the day and in the evening before bed can significantly impact sleep quality. Alcohol is a muscle relaxant; when the muscles relax, it can make you snore.
Alternatives to CPAP Therapy – Anti-snoring devices
If Sleep Apnoea is not the cause for your snoring, you may wish to look at some alternative anti-snoring devices which may help. These include positional sleep therapy and mandibular advancement devices. All of these items and more are available at Intus Healthcare.
Helpful articles:
How your sleeping position affects your sleep
The Best CPAP Masks for Side Sleepers
For more advice, contact us.